CoreText 的排版引擎:基礎
本章前言
使用 CoreText 技術,我們可以對富文本進行復雜的排版。經過一些簡單的擴展,我們還可以實現對於圖片,鏈接的點擊效果。CoreText 技術相對於 UIWebView,有著更少的內存占用,以及可以在後台渲染的優點,非常適合用於內容的排版工作。
本章我們將從最基本的開始,一步一步完成一個支持圖文混排、支持圖片和鏈接點擊的排版引擎。
CoreText 簡介
CoreText 是用於處理文字和字體的底層技術。它直接和 Core Graphics(又被稱為 Quartz)打交道。Quartz 是一個 2D 圖形渲染引擎,能夠處理 OSX 和 iOS 中的圖形顯示。
Quartz 能夠直接處理字體(font)和字形(glyphs),將文字渲染到界面上,它是基礎庫中唯一能夠處理字形的模塊。因此,CoreText 為了排版,需要將顯示的文本內容、位置、字體、字形直接傳遞給 Quartz。相比其它 UI 組件,由於 CoreText 直接和 Quartz 來交互,所以它具有高速的排版效果。
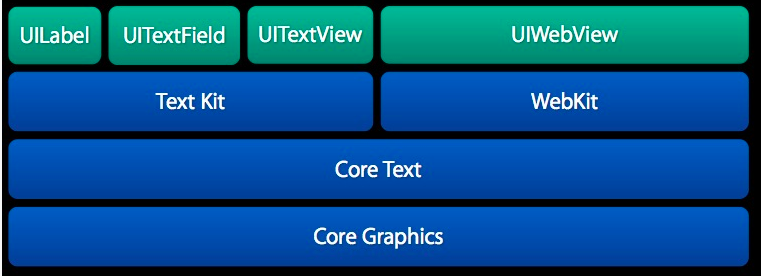
下圖是 CoreText 的架構圖,可以看到,CoreText 處於非常底層的位置,上層的 UI 控件(包括 UILabel,UITextField 以及 UITextView)和 UIWebView 都是基於 CoreText 來實現的。
注意:這個是 iOS7 之後的架構圖,在 iOS7 以前,並沒有圖中的 Text Kit 類,不過 CoreText 仍然是處在最底層直接和 Core Graphics 打交道的模塊。
UIWebView 也是處理復雜的文字排版的備選方案。對於排版,基於 CoreText 和基於 UIWebView 相比,前者有以下好處:
CoreText 占用的內存更少,渲染速度快,UIWebView 占用的內存更多,渲染速度慢。CoreText 在渲染界面前就可以精確地獲得顯示內容的高度(只要有了 CTFrame 即可),而 UIWebView 只有渲染出內容後,才能獲得內容的高度(而且還需要用 javascript 代碼來獲取)CoreText 的 CTFrame 可以在後台線程渲染,UIWebView 的內容只能在主線程(UI 線程)渲染。基於 CoreText 可以做更好的原生交互效果,交互效果可以更細膩。而 UIWebView 的交互效果都是用 javascript 來實現的,在交互效果上會有一些卡頓存在。例如,在 UIWebView 下,一個簡單的按鈕按下效果,都無法做到原生按鈕的即時和細膩的按下效果。當然,基於 CoreText 的排版方案也有一些劣勢:
CoreText 渲染出來的內容不能像 UIWebView 那樣方便地支持內容的復制。基於 CoreText 來排版需要自己處理很多復雜邏輯,例如需要自己處理圖片與文字混排相關的邏輯,也需要自己實現鏈接點擊操作的支持。在業界,很多應用都采用了基於 CoreText 技術的排版方案,例如:新浪微博客戶端,多看閱讀客戶端。我所在的創業公司的猿題庫,也使用了自己基於 CoreText 技術實現的排版引擎,下圖是我們產品的一個圖文混排的界面(其中所有公式都是用圖片的方式呈現的),可以看到,圖片和文字排版效果很好。
vcmVUZXh0IOTWyL61xL3nw+Y=" src="/uploadfile/Collfiles/20160427/20160427092605351.png" />
基於 CoreText 的基礎排版引擎
不帶圖片的排版引擎
下面我們來嘗試完成一個基於 CoreText 的排版引擎。我們將從最簡單的排版功能開始,然後逐步支持圖文混排,鏈接點擊等功能。
首先我們來嘗試完成一個不支持圖片內容的純文字排版引擎。
注意 1:由於整個排版引擎的代碼太多,為方便讀者閱讀,文章中只會列出最關鍵的核心代碼,完整的代碼請參考本書對應的 github 項目,項目地址是:https://github.com/tangqiaoboy/iOS-Pro 。
能輸出 Hello World 的 CoreText 工程
操作步驟
我們首先新建一個 Xcode 工程,步驟如下:
打開 Xcode,選擇 “File”->”New”->”Project”, 在彈出的對話框中,選擇 “Single View Application”,然後點擊 “Next”。(圖 2)接著填上項目名 CoreTextDemo,然後點擊 “Next”。(圖 3)選擇保存目錄後,我們就成功創建了一個空的工程。
圖 2
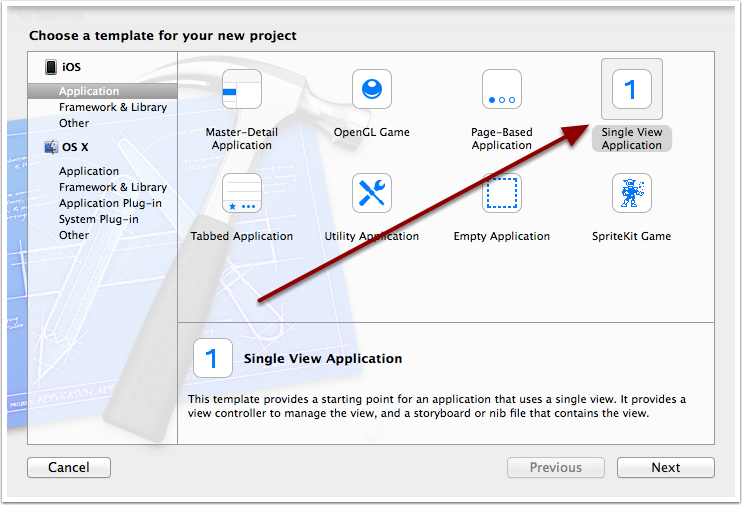
圖 3
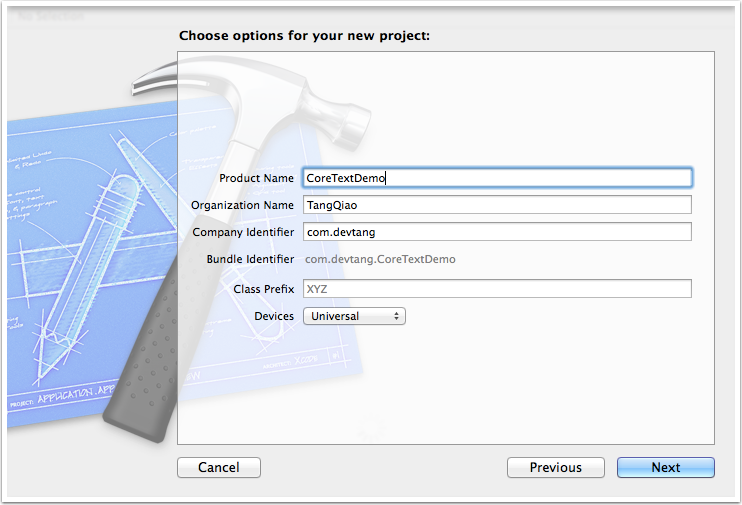
在工程目錄 “CoreTextDemo” 上右擊,選擇 “New File”, 然後填入類名CTDisplayView, 並且讓它的父類是 UIView。(如下圖)
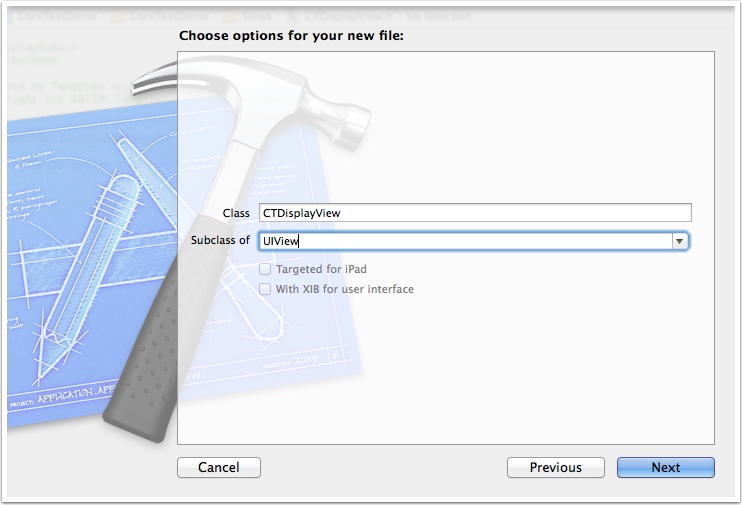
接著,我們在CTDisplayView.m文件中,讓其 import 頭文件CoreText/CoreText.h,接著輸入以下代碼來實現其drawRect方法:
#import "CTDisplayView.h"
#import "CoreText/CoreText.h"
@implementation CTDisplayView
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
[super drawRect:rect];
// 步驟 1
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
// 步驟 2
CGContextSetTextMatrix(context, CGAffineTransformIdentity);
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 0, self.bounds.size.height);
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 1.0, -1.0);
// 步驟 3
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, self.bounds);
// 步驟 4
NSAttributedString *attString = [[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"Hello World!"];
CTFramesetterRef framesetter =
CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)attString);
CTFrameRef frame =
CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter,
CFRangeMake(0, [attString length]), path, NULL);
// 步驟 5
CTFrameDraw(frame, context);
// 步驟 6
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(path);
CFRelease(framesetter);
}
@end
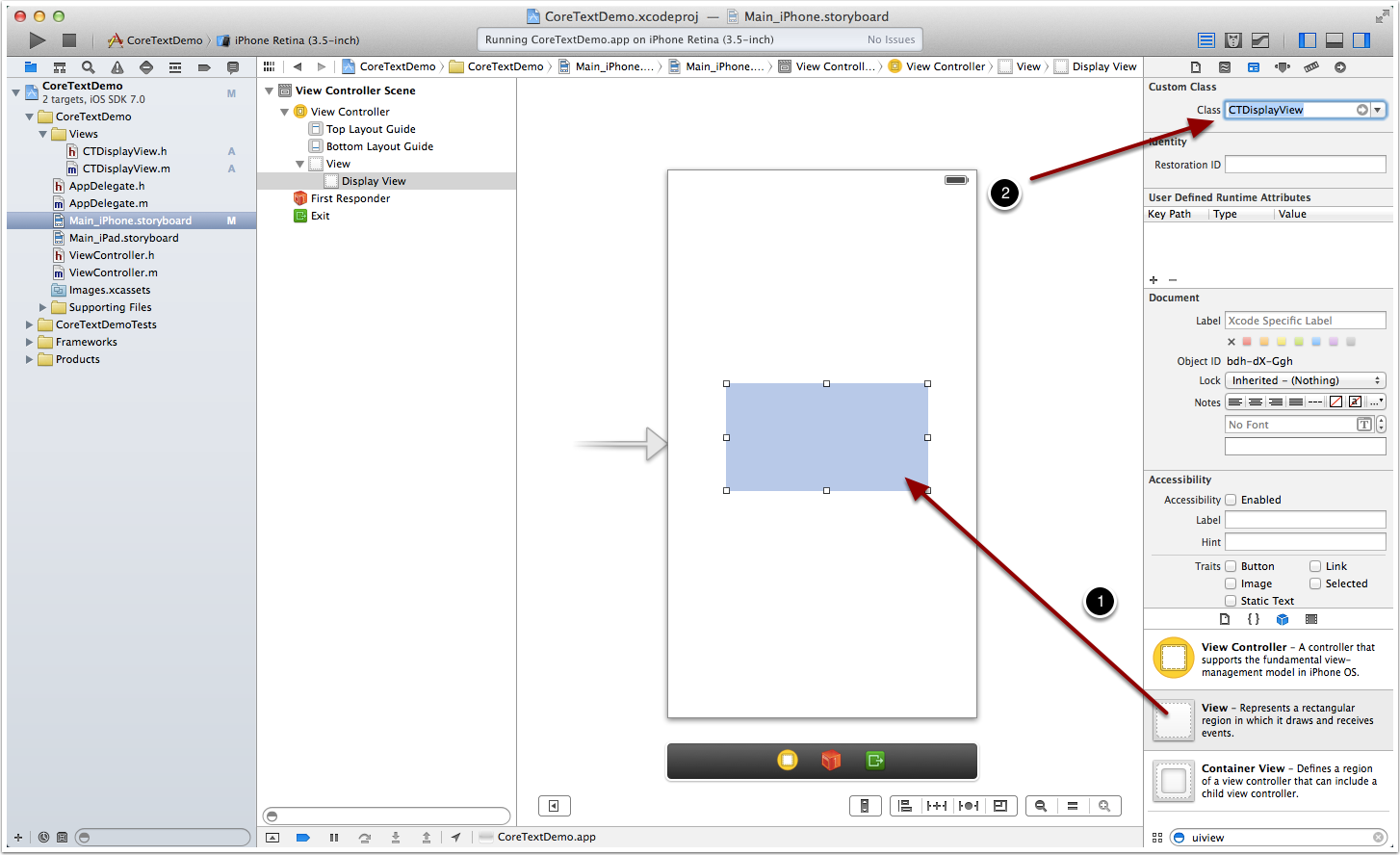
打開程序的 Storyboard 文件:Main_iPhone.storyboard:執行下面 2 步:
UIView修改為CTDisplayView。(如下圖步驟 2)
之後,我們運行程序,就可以看到,Hello World 出現在程序正中間了。如下圖。

###代碼解釋
下面解釋一下drawRect方法主要的步驟:
將坐標系上下翻轉。對於底層的繪制引擎來說,屏幕的左下角是(0, 0)坐標。而對於上層的 UIKit 來說,左上角是 (0, 0) 坐標。所以我們為了之後的坐標系描述按 UIKit 來做,所以先在這裡做一個坐標系的上下翻轉操作。翻轉之後,底層和上層的 (0, 0) 坐標就是重合的了。
為了加深理解,我們將這部分的代碼塊注釋掉,你會發現,整個Hello World界面將上下翻轉,如下圖所示。

為了加深理解,我們將該步驟的代碼替換成如下代碼,測試設置不同的繪制區域帶來的界面變化。
// 步驟 3
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddEllipseInRect(path, NULL, self.bounds);
// 步驟 4
NSAttributedString *attString = [[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:@"Hello World! "
" 創建繪制的區域,CoreText 本身支持各種文字排版的區域,"
" 我們這裡簡單地將 UIView 的整個界面作為排版的區域。"
" 為了加深理解,建議讀者將該步驟的代碼替換成如下代碼,"
" 測試設置不同的繪制區域帶來的界面變化。"];
執行結果如下圖所示:

代碼基本的宏定義和 Category
為了方便我們的代碼編寫,我在CoreTextDemo-Prefix.pch文件中增加了以下基本的宏定義,以方便我們使用 NSLog 和 UIColor。
#ifdef DEBUG #define debugLog(...) NSLog(__VA_ARGS__) #define debugMethod() NSLog(@"%s", __func__) #else #define debugLog(...) #define debugMethod() #endif #define RGB(A, B, C) [UIColor colorWithRed:A/255.0 green:B/255.0 blue:C/255.0 alpha:1.0]
我也為 UIView 的 frame 調整增加了一些擴展,可以方便地調整 UIView 的 x, y, width, height 等值。部分關鍵代碼如下(完整的代碼請查看示例工程):
UIView+frameAdjust.h 文件:
#import@interface UIView (frameAdjust) - (CGFloat)x; - (void)setX:(CGFloat)x; - (CGFloat)y; - (void)setY:(CGFloat)y; - (CGFloat)height; - (void)setHeight:(CGFloat)height; - (CGFloat)width; - (void)setWidth:(CGFloat)width; @end
UIView+frameAdjust.m 文件:
@implementation UIView (frameAdjust)
- (CGFloat)x {
return self.frame.origin.x;
}
- (void)setX:(CGFloat)x {
self.frame = CGRectMake(x, self.y, self.width, self.height);
}
- (CGFloat)y {
return self.frame.origin.y;
}
- (void)setY:(CGFloat)y {
self.frame = CGRectMake(self.x, y, self.width, self.height);
}
- (CGFloat)height {
return self.frame.size.height;
}
- (void)setHeight:(CGFloat)height {
self.frame = CGRectMake(self.x, self.y, self.width, height);
}
- (CGFloat)width {
return self.frame.size.width;
}
- (void)setWidth:(CGFloat)width {
self.frame = CGRectMake(self.x, self.y, width, self.height);
}
@end
文章中的其余代碼默認都#import 了以上提到的宏定義和 UIView Category。
排版引擎框架
上面的 Hello World 工程僅僅展示了 Core Text 排版的基本能力。但是要制作一個較完善的排版引擎,我們不能簡單的將所有代碼都放到 CTDisplayView 的drawRect方法裡面。根據設計模式中的 “ 單一功能原則 “(Single responsibility principle),我們應該把功能拆分,把不同的功能都放到各自不同的類裡面。
對於一個復雜的排版引擎來說,可以將其功能拆成以下幾個類來完成:
一個顯示用的類,僅負責顯示內容,不負責排版一個模型類,用於承載顯示所需要的所有數據一個排版類,用於實現文字內容的排版一個配置類,用於實現一些排版時的可配置項注:” 單一功能原則 “(Single responsibility principle)
參考鏈接:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%8D%95%E4%B8%80%E5%8A%9F%E8%83%BD%E5%8E%9F%E5%88%99
按照以上原則,我們將CTDisplayView中的部分內容拆開,由 4 個類構成:
CTFrameParserConfig類,用於配置繪制的參數,例如:文字顏色,大小,行間距等。CTFrameParser類,用於生成最後繪制界面需要的CTFrameRef實例。CoreTextData類,用於保存由CTFrameParser類生成的CTFrameRef實例以及CTFrameRef實際繪制需要的高度。CTDisplayView類,持有CoreTextData類的實例,負責將CTFrameRef繪制到界面上。
關於這 4 個類的關鍵代碼如下:
CTFrameParserConfig類:
#import@interface CTFrameParserConfig : NSObject @property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat width; @property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat fontSize; @property (nonatomic, assign) CGFloat lineSpace; @property (nonatomic, strong) UIColor *textColor; @end
#import "CTFrameParserConfig.h"
@implementation CTFrameParserConfig
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
_width = 200.0f;
_fontSize = 16.0f;
_lineSpace = 8.0f;
_textColor = RGB(108, 108, 108);
}
return self;
}
@end
CTFrameParser類:
#import#import "CoreTextData.h" #import "CTFrameParserConfig.h" @interface CTFrameParser : NSObject + (CoreTextData *)parseContent:(NSString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config; @end
#import "CTFrameParser.h"
#import "CTFrameParserConfig.h"
@implementation CTFrameParser
+ (NSDictionary *)attributesWithConfig:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config {
CGFloat fontSize = config.fontSize;
CTFontRef fontRef = CTFontCreateWithName((CFStringRef)@"ArialMT", fontSize, NULL);
CGFloat lineSpacing = config.lineSpace;
const CFIndex kNumberOfSettings = 3;
CTParagraphStyleSetting theSettings[kNumberOfSettings] = {
{ kCTParagraphStyleSpecifierLineSpacingAdjustment, sizeof(CGFloat), &lineSpacing },
{ kCTParagraphStyleSpecifierMaximumLineSpacing, sizeof(CGFloat), &lineSpacing },
{ kCTParagraphStyleSpecifierMinimumLineSpacing, sizeof(CGFloat), &lineSpacing }
};
CTParagraphStyleRef theParagraphRef = CTParagraphStyleCreate(theSettings, kNumberOfSettings);
UIColor * textColor = config.textColor;
NSMutableDictionary * dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
dict[(id)kCTForegroundColorAttributeName] = (id)textColor.CGColor;
dict[(id)kCTFontAttributeName] = (__bridge id)fontRef;
dict[(id)kCTParagraphStyleAttributeName] = (__bridge id)theParagraphRef;
CFRelease(theParagraphRef);
CFRelease(fontRef);
return dict;
}
+ (CoreTextData *)parseContent:(NSString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
NSDictionary *attributes = [self attributesWithConfig:config];
NSAttributedString *contentString =
[[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content
attributes:attributes];
// 創建 CTFramesetterRef 實例
CTFramesetterRef framesetter = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)contentString);
// 獲得要繪制的區域的高度
CGSize restrictSize = CGSizeMake(config.width, CGFLOAT_MAX);
CGSize coreTextSize = CTFramesetterSuggestFrameSizeWithConstraints(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0,0), nil, restrictSize, nil);
CGFloat textHeight = coreTextSize.height;
// 生成 CTFrameRef 實例
CTFrameRef frame = [self createFrameWithFramesetter:framesetter config:config height:textHeight];
// 將生成好的 CTFrameRef 實例和計算好的繪制高度保存到 CoreTextData 實例中,最後返回 CoreTextData 實例
CoreTextData *data = [[CoreTextData alloc] init];
data.ctFrame = frame;
data.height = textHeight;
// 釋放內存
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(framesetter);
return data;
}
+ (CTFrameRef)createFrameWithFramesetter:(CTFramesetterRef)framesetter
config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config
height:(CGFloat)height {
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, CGRectMake(0, 0, config.width, height));
CTFrameRef frame = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, 0), path, NULL);
CFRelease(path);
return frame;
}
@end
CoreTextData類:
#import@interface CoreTextData : NSObject @property (assign, nonatomic) CTFrameRef ctFrame; @property (assign, nonatomic) CGFloat height; @end
#import "CoreTextData.h"
@implementation CoreTextData
- (void)setCtFrame:(CTFrameRef)ctFrame {
if (_ctFrame != ctFrame) {
if (_ctFrame != nil) {
CFRelease(_ctFrame);
}
CFRetain(ctFrame);
_ctFrame = ctFrame;
}
}
- (void)dealloc {
if (_ctFrame != nil) {
CFRelease(_ctFrame);
_ctFrame = nil;
}
}
@end
CTDisplayView類:
#import#import "CoreTextData.h" @interface CTDisplayView : UIView @property (strong, nonatomic) CoreTextData * data; @end
#import "CTDisplayView.h"
@implementation CTDisplayView
- (void)drawRect:(CGRect)rect
{
[super drawRect:rect];
CGContextRef context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext();
CGContextSetTextMatrix(context, CGAffineTransformIdentity);
CGContextTranslateCTM(context, 0, self.bounds.size.height);
CGContextScaleCTM(context, 1.0, -1.0);
if (self.data) {
CTFrameDraw(self.data.ctFrame, context);
}
}
@end
以上 4 個類中的邏輯與之前 Hello World 那個項目的邏輯基本一致,只是分拆到了 4 個類中完成。另外,CTFrameParser 增加了方法來獲得要繪制的區域的高度,並將高度信息保存到CoreTextData類的實例中。之所以要獲得繪制區域的高度,是因為在很多實際使用場景中,我們需要先知道所要顯示內容的高度,之後才可以進行繪制。
例如,在 UITableView 在渲染時,UITableView 首先會向 delegate 回調如下方法來獲得每個將要渲染的 cell 的高度:
- (CGFloat)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView heightForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;
之後,UITableView 會計算當前滾動的位置具體需要繪制的 UITableViewCell 是哪些,然後對於那些需要繪制的 Cell,UITableView 才會繼續向其 data source 回調如下方法來獲得 UITableViewCell 實例:
- (UITableViewCell *)cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath;
對於上面的情況,如果我們使用 CoreText 來作為 TableViewCell 的內容,那麼就必須在每個 Cell 繪制之前,就知道其需要的繪制高度,否則 UITableView 將無法正常工作。
完成以上 4 個類之後,我們就可以簡單地在ViewController.m文件中,加入如下代碼來配置CTDisplayView的顯示內容,位置,高度,字體,顏色等信息。代碼如下所示。
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet CTDisplayView *ctView;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
CTFrameParserConfig *config = [[CTFrameParserConfig alloc] init];
config.textColor = [UIColor redColor];
config.width = self.ctView.width;
CoreTextData *data = [CTFrameParser parseContent:@" 按照以上原則,我們將`CTDisplayView`中的部分內容拆開。" config:config];
self.ctView.data = data;
self.ctView.height = data.height;
self.ctView.backgroundColor = [UIColor yellowColor];
}
@end
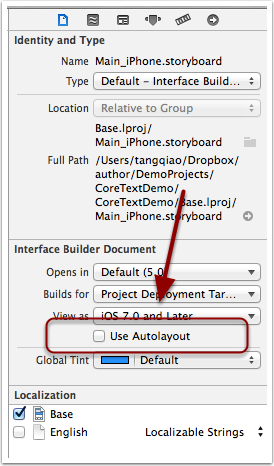
注意:從 Xcode4.0 開始,默認的界面編輯就開啟了對於Use Autolayout的使用,但因為我們在代碼中直接修改了變量ctView的 frame 信息,所以需要在Main_iPhone.storyboard中將Use Autolayout這一項取消勾選。如下圖所示:
以下是本框架的 UML 示意圖,從圖中我們可以看出,這 4 個 Core Text 類的關系是這樣的:
CTFrameParser通過CTFrameparserConfig實例來生成CoreTextData實例。CTDisplayView通過持有CoreTextData實例來獲得繪制所需要的所有信息。ViewController類通過配置CTFrameparserConfig實例,進而獲得生成的CoreTextData實例,最後將其賦值給他的CTDisplayView成員,達到將指定內容顯示在界面上的效果。
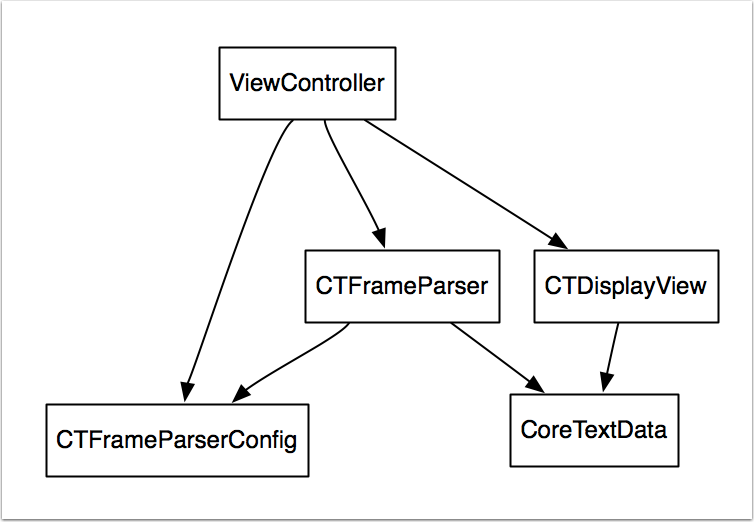
說明 1:整個工程代碼在名為basic_arch的分支下,讀者可以在示例的源代碼工程中使用git checkout basic_arch來切換到當前講解的工程示例代碼。
說明 2:為了方便操作UIView的frame屬性,項目中增加了一個名為UIView+frameAdjust.m文件,它通過Category來給UIView增加了直接設置height屬性的方法。
定制排版文件格式
對於上面的例子,我們給 CTFrameParser 使增加了一個將 NSString 轉換為 CoreTextData 的方法。但這樣的實現方式有很多局限性,因為整個內容雖然可以定制字體大小,顏色,行高等信息,但是卻不能支持定制內容中的某一部分。例如,如果我們只想讓內容的前三個字顯示成紅色,而其它文字顯示成黑色,那麼就辦不到了。
解決的辦法很簡單,我們讓CTFrameParser支持接受 NSAttributeString 作為參數,然後在ViewController類中設置我們想要的 NSAttributeString 信息。
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
CTFrameParserConfig *config = [[CTFrameParserConfig alloc] init];
config.width = self.ctView.width;
config.textColor = [UIColor blackColor];
NSString *content =
@" 對於上面的例子,我們給 CTFrameParser 增加了一個將 NSString 轉 "
" 換為 CoreTextData 的方法。"
" 但這樣的實現方式有很多局限性,因為整個內容雖然可以定制字體 "
" 大小,顏色,行高等信息,但是卻不能支持定制內容中的某一部分。"
" 例如,如果我們只想讓內容的前三個字顯示成紅色,而其它文字顯 "
" 示成黑色,那麼就辦不到了。"
"\n\n"
" 解決的辦法很簡單,我們讓`CTFrameParser`支持接受 "
"NSAttributeString 作為參數,然後在 NSAttributeString 中設置好 "
" 我們想要的信息。";
NSDictionary *attr = [CTFrameParser attributesWithConfig:config];
NSMutableAttributedString *attributedString =
[[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content
attributes:attr];
[attributedString addAttribute:NSForegroundColorAttributeName
value:[UIColor redColor]
range:NSMakeRange(0, 7)];
CoreTextData *data = [CTFrameParser parseAttributedContent:attributedString
config:config];
self.ctView.data = data;
self.ctView.height = data.height;
self.ctView.backgroundColor = [UIColor yellowColor];
}
@end
結果如下圖所示,我們很方便就把前面 7 個字變成了紅色。

更進一步地,實際工作中,我們更希望通過一個排版文件,來設置需要排版的文字的內容、顏色、字體大小等信息。我在開發猿題庫應用時,自己定義了一個基於 UBB 的排版模版,但是實現該排版文件的解析器要花費大量的篇幅,考慮到這並不是本章的重點,所以我們以一個較簡單的排版文件來講解其思想。
我們規定排版的模版文件為 JSON 格式。JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一種輕量級的數據交換格式,易於閱讀和編寫,同時也易於機器解析和生成。iOS 從 5.0 開始,提供了名為NSJSONSerialization的類庫來方便開發者對 JSON 的解析。在 iOS5.0 之前,業界也有很多相關的 JSON 解析開源庫,例如 JSONKit 可供大家使用。
我們的排版模版示例文件如下所示:
[ { "color" : "blue",
"content" : " 更進一步地,實際工作中,我們更希望通過一個排版文件,來設置需要排版的文字的 ",
"size" : 16,
"type" : "txt"
},
{ "color" : "red",
"content" : " 內容、顏色、字體 ",
"size" : 22,
"type" : "txt"
},
{ "color" : "black",
"content" : " 大小等信息。\n",
"size" : 16,
"type" : "txt"
},
{ "color" : "default",
"content" : " 我在開發猿題庫應用時,自己定義了一個基於 UBB 的排版模版,但是實現該排版文件的解析器要花費大量的篇幅,考慮到這並不是本章的重點,所以我們以一個較簡單的排版文件來講解其思想。",
"type" : "txt"
}
]
通過蘋果提供的NSJSONSerialization類,我們可以將上面的模版文件轉換成 NSArray 數組,每一個數組元素是一個 NSDictionary,代表一段相同設置的文字。為了簡單,我們的配置文件只支持配置顏色和字號,但是讀者可以依據同樣的思想,很方便地增加其它配置信息。
接下來我們要為CTFrameParser增加一個方法,讓其可以從如上格式的模版文件中生成CoreTextData。最終我們的實現代碼如下:
// 方法一
+ (CoreTextData *)parseTemplateFile:(NSString *)path config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
NSAttributedString *content = [self loadTemplateFile:path config:config];
return [self parseAttributedContent:content config:config];
}
// 方法二
+ (NSAttributedString *)loadTemplateFile:(NSString *)path config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSMutableAttributedString *result = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] init];
if (data) {
NSArray *array = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data
options:NSJSONReadingAllowFragments
error:nil];
if ([array isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
for (NSDictionary *dict in array) {
NSString *type = dict[@"type"];
if ([type isEqualToString:@"txt"]) {
NSAttributedString *as =
[self parseAttributedContentFromNSDictionary:dict
config:config];
[result appendAttributedString:as];
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
// 方法三
+ (NSAttributedString *)parseAttributedContentFromNSDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict
config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
NSMutableDictionary *attributes = [self attributesWithConfig:config];
// set color
UIColor *color = [self colorFromTemplate:dict[@"color"]];
if (color) {
attributes[(id)kCTForegroundColorAttributeName] = (id)color.CGColor;
}
// set font size
CGFloat fontSize = [dict[@"size"] floatValue];
if (fontSize > 0) {
CTFontRef fontRef = CTFontCreateWithName((CFStringRef)@"ArialMT", fontSize, NULL);
attributes[(id)kCTFontAttributeName] = (__bridge id)fontRef;
CFRelease(fontRef);
}
NSString *content = dict[@"content"];
return [[NSAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content attributes:attributes];
}
// 方法四
+ (UIColor *)colorFromTemplate:(NSString *)name {
if ([name isEqualToString:@"blue"]) {
return [UIColor blueColor];
} else if ([name isEqualToString:@"red"]) {
return [UIColor redColor];
} else if ([name isEqualToString:@"black"]) {
return [UIColor blackColor];
} else {
return nil;
}
}
// 方法五
+ (CoreTextData *)parseAttributedContent:(NSAttributedString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
// 創建 CTFramesetterRef 實例
CTFramesetterRef framesetter = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)content);
// 獲得要緩制的區域的高度
CGSize restrictSize = CGSizeMake(config.width, CGFLOAT_MAX);
CGSize coreTextSize = CTFramesetterSuggestFrameSizeWithConstraints(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0,0), nil, restrictSize, nil);
CGFloat textHeight = coreTextSize.height;
// 生成 CTFrameRef 實例
CTFrameRef frame = [self createFrameWithFramesetter:framesetter config:config height:textHeight];
// 將生成好的 CTFrameRef 實例和計算好的緩制高度保存到 CoreTextData 實例中,最後返回 CoreTextData 實例
CoreTextData *data = [[CoreTextData alloc] init];
data.ctFrame = frame;
data.height = textHeight;
// 釋放內存
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(framesetter);
return data;
}
// 方法六
+ (CTFrameRef)createFrameWithFramesetter:(CTFramesetterRef)framesetter
config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config
height:(CGFloat)height {
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, CGRectMake(0, 0, config.width, height));
CTFrameRef frame = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, 0), path, NULL);
CFRelease(path);
return frame;
}
以上代碼主要由 6 個子方法構成:
方法一用於提供對外的接口,調用方法二實現從一個 JSON 的模版文件中讀取內容,然後調用方法五生成CoreTextData。方法二讀取 JSON 文件內容,並且調用方法三獲得從NSDictionary到NSAttributedString的轉換結果。方法三將NSDictionary內容轉換為NSAttributedString。方法四提供將NSString轉為UIColor的功能。方法五接受一個NSAttributedString和一個config參數,將NSAttributedString轉換成CoreTextData返回。方法六是方法五的一個輔助函數,供方法五調用。
然後我們將ViewController中的調用代碼作一下更改,使其從模版文件中加載內容,如下所示:
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
CTFrameParserConfig *config = [[CTFrameParserConfig alloc] init];
config.width = self.ctView.width;
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"content" ofType:@"json"];
CoreTextData *data = [CTFrameParser parseTemplateFile:path config:config];
self.ctView.data = data;
self.ctView.height = data.height;
self.ctView.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
}
@end
最後運行得到的結果如下所示,可以看到,通過一個簡單的模板文件,我們已經可以很方便地定義排版的配置信息了。

- iOS9與XCode7中不克不及應用http銜接的疾速處理方法
- xcode8 封閉掌握台不打印不信息的處理辦法(圖文詳解)
- 史上最具體的CocoaPods裝置教程(圖文)
- IOS Xcode中快捷鍵年夜全
- iOS中處理Xcode 8掌握台亂碼的方法
- IOS開辟之適配iOS10及Xcode8的留意點
- xcode8提交ipa掉敗沒法構建版本成績的處理計劃
- IOS 開辟自界說條形ProgressView的實例
- XCode 加速編譯鏈接速度的辦法
- 2016 cocoapods的裝置和應用辦法和版本進級碰到的成績
- IOS 陀螺儀開辟(CoreMotion框架)實例詳解
- 進修iOS自界說導航掌握器UINavigationController
- Xcode 8打印log日記的成績小結及處理辦法
- iOS10 適配和Xcode8設置裝備擺設總結
- iOS Xcode8更新後輸入log日記封閉的辦法